The integrative Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience (iCAN) Lab aims to understand how the brain supports learning, memory, and interactions with emotion, and how these processes develop from childhood through adolescence into adulthood. The overarching goal is to optimize learning, memory and emotional wellbeing in education, and to foster brain-inspired prevention and early intervention of emotional disturbance or disorders.
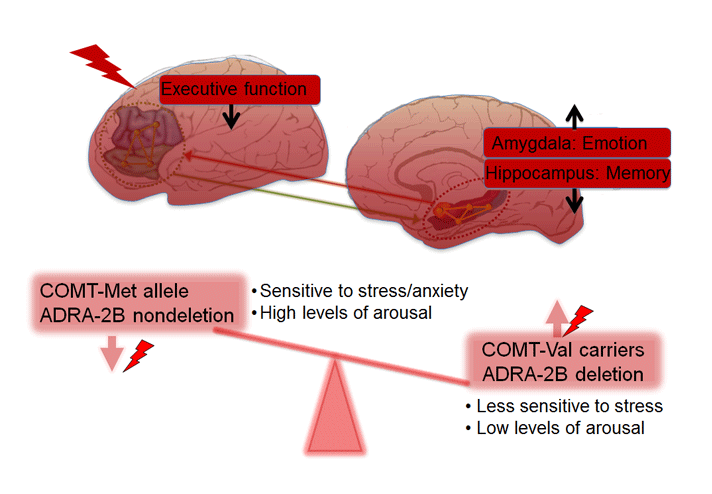
Stress, brain and cognition

Exposure to excessive stress is a key risk factor of mental illness, and leads to brain dysfunctions and poor health outcomes such as anxiety and depression. Using a multi-disciplinary approach with fMRI, cognitive, psychophysiology and genetic techniques, we aim to investigate neurobiological mechanisms underlying stress-induced adaptation and dysfunctions in the brain and cognition, and associated genetic signatures in healthy, sub-clinical and clinical populations.
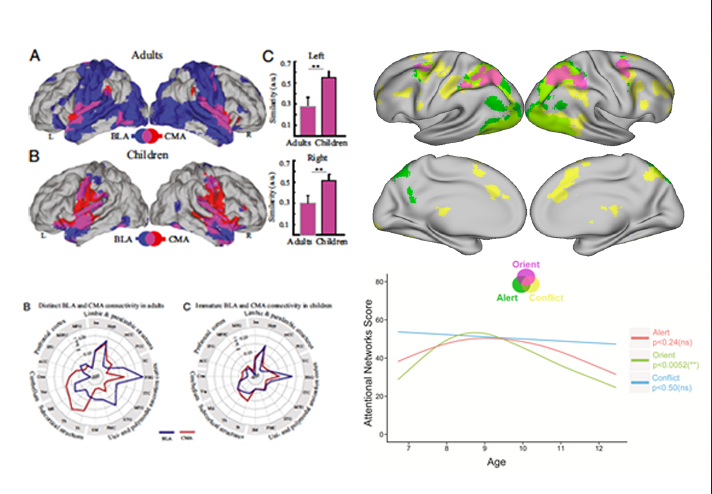
Emotion-related brain development

"Understanding brain cognitive & affective development is to empower children's learning and mental health." Using cutting-edging brain imaging and cognitive techniques, our "development" team aims to investigate typical and atypical neurodevelopment of cognitive (i.e., attention, working memory) and affective (i.e., emotional memory & regulation) functions from childhood to adulthood.
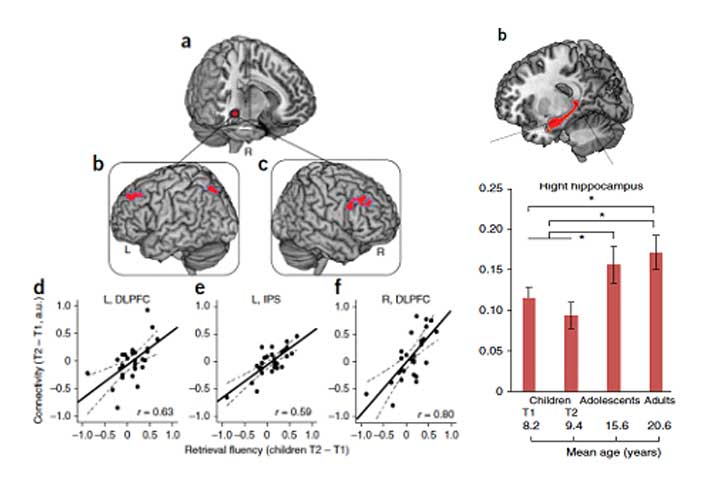
Children's brain cognitive & affective development

"Understanding brain cognitive & affective development is to empower children's learning and mental health." Using cutting-edging brain imaging and cognitive techniques, we aim to investigate typical and atypical neurodevelopment of cognitive (i.e., attention, working memory) and affective (i.e., emotional memory & regulation) functions from childhood to adulthood.
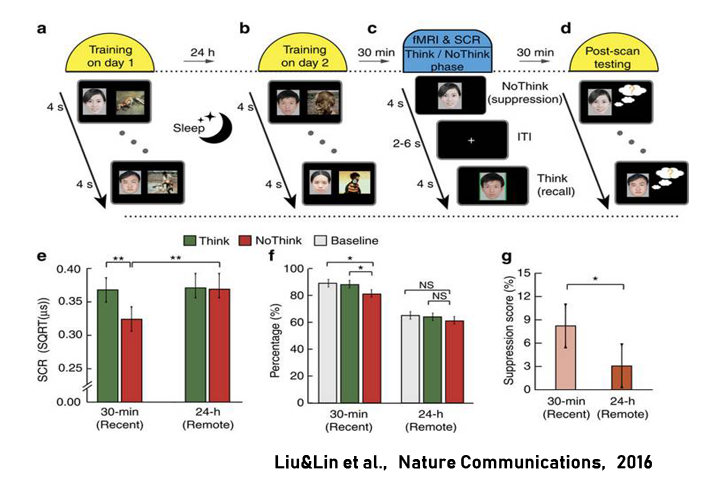
Emotion, sleep & memory

Utilizing functional brain imaging, psychophysiology, sleep EEG, cognitive & behavioral techniques, we aim to investigate how brain networks, especially the medial temporal lobe, amygdala, prefrontal and parietal systems, dynamically coordinate to support learning and memory, and how emotion and sleep affect the transform of newly acquired information into long-term memory.